4608, Phase-IV, GIDC, Vatva, Ahmedabad-382445, Gujarat-India
-
-
Mon - Sat 10:00 - 7:30, Sunday - CLOSED
4608, Phase-IV, GIDC, Vatva, Ahmedabad-382445, Gujarat-India
Mon - Sat 10:00 - 7:30, Sunday - CLOSED
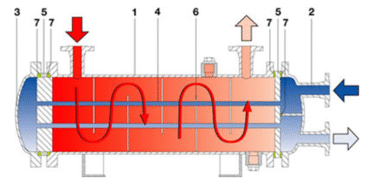
A heat exchanger is an unfired pressure system used to enable efficient heat transfer between two media that flow past one another. These media are partitioned by a thin wall through which heat exchange takes place by virtue of the temperature difference but not any mixing.
This helps in achieving the best thermal performance and energy efficiency in a variety of industrial processes. As can be seen from the diagram, one medium passes through the shell chamber and the other through the tube chamber. The flow in the shell chamber is deliberately directed by baffles to achieve the maximum cross-flow over the tubes for optimum heat transfer efficiency. This type of design and arrangement of these baffles depends on the type of application. Depending on the operational needs, such as flow dynamics, velocity, and pressure loss requirements, the tube chamber may be designed for single-pass or multi-pass flow. With the exception of minor radiation losses, the transferred heat energy is the same, which ensures maximum thermal performance and efficiency.
Effective heat exchange is only possible when there is a sufficient temperature difference between the two media. The larger the temperature difference, the smaller the heat transfer surface needed, which enables a more compact and space-saving apparatus design.
The thermal performance of a heat exchanger is established by the product of the mean logarithmic temperature difference, the heat transfer surface area, and the heat transfer coefficient. The heat transfer coefficient, on the other hand, is determined by the flow characteristics of the media, which are governed by the design parameters of the exchanger. Optimal values for these parameters provide maximum thermal efficiency and performance.